| Description | Biotin is a water-soluble, enzyme co-factor present in minute amounts in every living cell. Target: Others Biotin is necessary for cell growth, the production of fatty acids, and the metabolism of fats and amino acids. It plays a role in the citric acid cycle, which is the process by which biochemical energy is generated during aerobic respiration. Biotin is a coenzyme for carboxylase enzymes, involved in the synthesis of fatty acids, isoleucine, and valine, and in gluconeogenesis. In addition, biotin is widely used throughout the biotechnology industry to conjugate proteins for biochemical assays. The dietary biotin intake in Western populations has been estimated to be 35 to 70 microg/d (143-287 nmol/d). Recent studies suggest that humans absorb biotin nearly completely. Conditions that may increase biotin requirements in humans include pregnancy, lactation, and therapy with anticonvulsants or lipoic acid [1, 2]. | ||||||||||||||||
| Preparing Stock Solutions |
Please refer to the solubility information to select the appropriate solvent. |
||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Weight | 244.31 | ||||||||||||||||
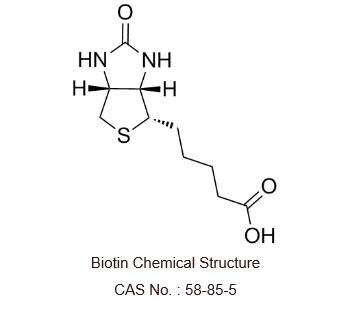
| Formula | C₁₀H₁₆N₂O₃S | ||||||||||||||||
| CAS No. | 58-85-5 | ||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | O=C(O)CCCC[C@@H]1SC[C@]([C@]1([H])N2)([H])NC2=O | ||||||||||||||||
| Storage |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Shipping | Room temperature in continental US; may vary elsewhere | ||||||||||||||||
| Solvent & Solubility | DMSO: ≥ 43 mg/mL
* “<1 mg/mL” means slightly soluble or insoluble. “≥” means soluble, but saturation unknown. |