| Description | Colistin, a polypeptide antibiotic, is bactericidal to gram-negative bacteria by interfering with the structure and function of the outer and cytoplasmic membranes of bacteria. | ||||||||||||||||
| In Vitro | Colistins are bactericidal to gram-negative bacteria by a detergent-like mechanism. This mechanism involves interaction with lipopolysaccharides and phospholipids of the outer membrane and electrostatic interference with the outer membrane by competitively displacing divalent cations (calcium and magnesium) from the negatively charged phosphate groups of membrane lipids[1]. Colistin (polymyxin E) owns favorable properties of rapid bacterial killing, a narrow spectrum of activity, and an associated slow development of resistance for the treatment of infections caused by multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria. There are two forms of colistin available commercially: colistin (sulfate) mainly for topical use and colistin methanesulfonate (sodium) for parenteral use[2]. | ||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo | High concentrations of colistin in rat ELF are achieved as a result of slow and sustained CMS conversion following i.t. instillation[3]. Colistin is often used in piglets but underdosing and overdosing are frequent. Under- or overdoses of colistin do not result in any major disturbance of piglet fecal microbiota and rarely select for chromosomal resistance in the dominant E. coli population[4]. | ||||||||||||||||
| Preparing Stock Solutions |
Please refer to the solubility information to select the appropriate solvent. |
||||||||||||||||
| Animal Administration [3] |
Rats: Colistin methanesulfonate (sodium) and colistin (sulfate) dosing solutions are freshly prepared in sterile 0.9% sodium chloride. For the i.v. studies, colistin methanesulfonate (CMS) or sulfate solutions are administered by a bolus injection via the jugular vein cannula. Intratracheal (i.t.) instillation is utilized as the technique for pulmonary administration. Animals are administered i.v. CMS at doses of 14 mg/kg of body weight, 28 mg/kg or 56 mg/kg. In an independent study, rats are administered i.v. colistin at doses of 0.21 mg/kg, 0.41 mg/kg, or 0.62 mg/kg[3]. MCE has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. | ||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Weight | 1253.51 | ||||||||||||||||
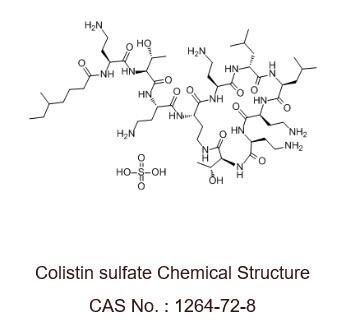
| Formula | C₅₂H₁₀₀N₁₆O₁₇S | ||||||||||||||||
| CAS No. | 1264-72-8 | ||||||||||||||||
| Storage |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Shipping | Room temperature in continental US; may vary elsewhere | ||||||||||||||||
| Solvent & Solubility | H2O: ≥ 32 mg/mL
* “<1 mg/mL” means slightly soluble or insoluble. “≥” means soluble, but saturation unknown. |